Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
- Integers in each row are sorted from left to right.
- The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
Example 1:

Input: matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3 Output: true
Example 2:
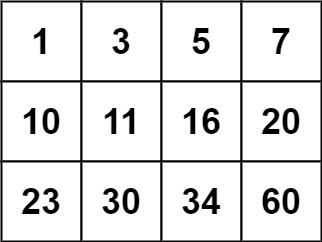
Input: matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13 Output: false
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-104 <= matrix[i][j], target <= 104
Solution 1: (DFS)
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var searchMatrix = function(matrix, target) {
return dfs(matrix, target, 0, 0);
};
function dfs(matrix, target, x, y) {
let rows = matrix.length;
let cols = matrix[0].length;
// exit recursion condition, reach to the end;
if (y === rows) return false;
// traverse from left to right, then next row
let nextX = (x + 1) % cols;
let nextY = nextX === 0 ? y + 1 : y;
// found return true or not found, DFS next element
if (matrix[y][x] === target)
return true;
else
return dfs(matrix, target, nextX, nextY);
return false;
}Solution 2: (Binary Search) Better and Faster!
- Time complexity: O(log(mn))
- Space complexity: O(1)
var searchMatrix = function(matrix, target) {
let cols = matrix[0].length;
// treat 2D as 1D, use binary search
let l = 0;
let r = matrix.length * cols;
while (l < r) {
let mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
let row = Math.floor(mid / cols);
let col = mid % cols;
if (matrix[row][col] === target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[row][col] > target) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
};