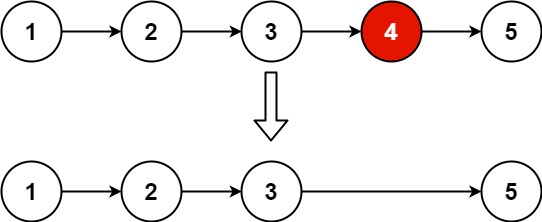
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:

Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 Output: true Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 Output: true Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
Example 3:

Input: head = [1], pos = -1 Output: false Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105posis-1or a valid index in the linked-list.
Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
Idea:
Use fast and slow pointers traversal, you they can meet each other then there is a circle
Solution:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function(head) {
let fast = head;
let slow = head;
while (fast) {
if (!fast.next) return false;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast === slow) return true;
}
return false;
};