Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,2,3] Output: [3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Example 4:
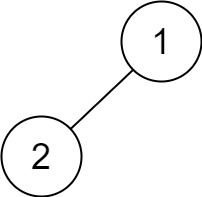
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [2,1]
Example 5:
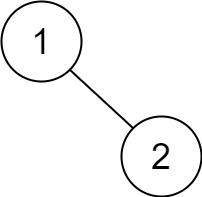
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: [2,1]
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Idea:
Use two stacks:
1. Push root to first stack. 2. Loop while first stack is not empty 2.1 Pop a node from first stack and push it to second stack(res[]) 2.2 Push left and right children of the popped node to first stack 3. Pop all elements from second stack(res.reverse())
Solution:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res = []; // use res as another stack
// empty tree case:
if (root === null) return res;
let stack = [];
// postorder visit: left, right, root
stack.push(root);
while (stack.length !== 0) {
let cur = stack.pop();
// treat it as stack, store them in reverse order:
// i.e root, left, right
res.push(cur.val);
if (cur.left) stack.push(cur.left);
if (cur.right) stack.push(cur.right);
}
// we can pop all elements one by one, or just reverse them
return res.reverse();
};