Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
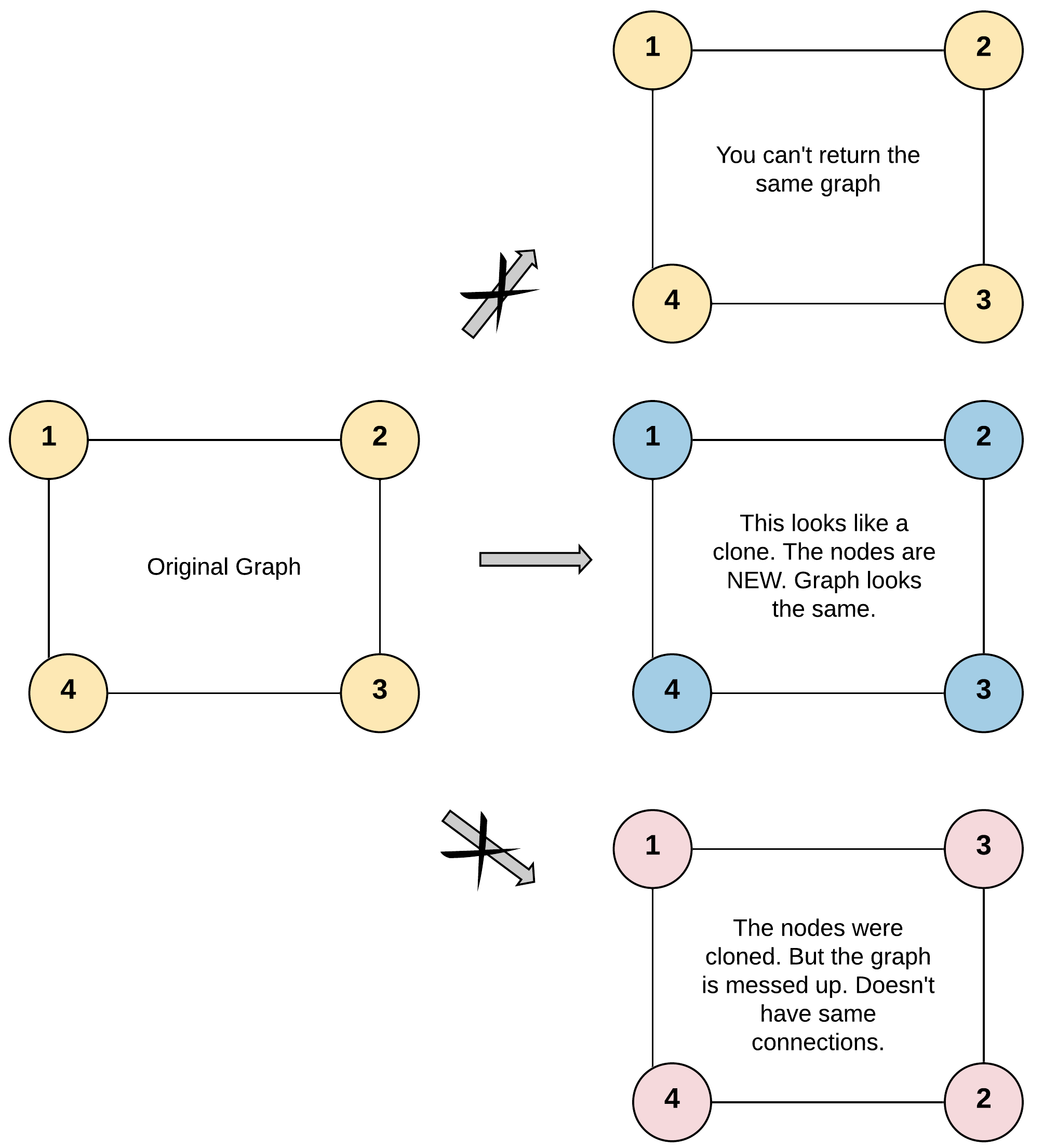
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
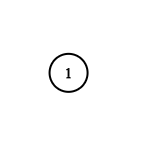
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
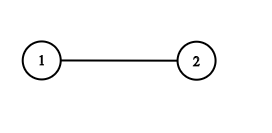
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Idea:
BFS Queue + HashMap +
我们使用 BFS 来遍历图,使用队列 queue 进行辅助,一个 HashMap 来建立原图结点和克隆结点之间的映射。先克隆当前结点,然后建立映射,并加入 queue 中,进行 while 循环。在循环中,取出队首结点,遍历其所有 neighbor 结点,若不在 HashMap 中,我们根据 neigbor 结点值克隆一个新 neighbor 结点,建立映射,并且排入 queue 中。然后将 neighbor 结点在 HashMap 中的映射结点加入到克隆结点的 neighbors 数组中即可,参见代码如下:
- Time complexity: O(V+E) 点+边
- Space complexity: O(V+E)
Solution 1:
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, neighbors) {
* this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
* this.neighbors = neighbors === undefined ? [] : neighbors;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} node
* @return {Node}
*/
var cloneGraph = function(node) {
if (node === null) return null;
let map = new Map();
map.set(node, new Node(node.val));
let q = []; // queue
q.push(node);
while (q.length !== 0) {
let cur = q.shift();
for (let n of cur.neighbors) {
if (!map.has(n)) {
map.set(n, new Node(n.val));
q.push(n);
}
map.get(cur).neighbors.push(map.get(n));
}
}
return map.get(node);
};Solution 2:
var cloneGraph = function(node) {
if (node === null) return null;
let visited = new Map();
let map = new Map();
let q = []; // queue
q.push(node);
while (q.length !== 0) {
let cur = q.shift();
if (visited.has(cur)) continue;
visited.set(cur, true);
if (!map.has(cur)) map.set(cur, new Node(cur.val));
let temp = map.get(cur);
for (let n of cur.neighbors) {
if (!map.has(n)) map.set(n, new Node(n.val));
q.push(n);
temp.neighbors.push(map.get(n));
}
}
return map.get(node);
};